Last Updated: 2021-05-10
🚧 Work In Progress
Creating a New Tutorial
This is a meta-tutorial on how to create a tutorial.
It is aimed at showing a lab member how they can create new tutorials without worrying about cloning this repository or using the command line. There are alternative ways to accomplish this, but this method can be done entirely within the github.com interface.
In most images, red dots signify where you should focus your attention/click.
[00] Copying the Template
- Navigate to
UWRobotLearning/UWRobotLearning.github.io/Tutorials/ - Click
_tutorial_template.md
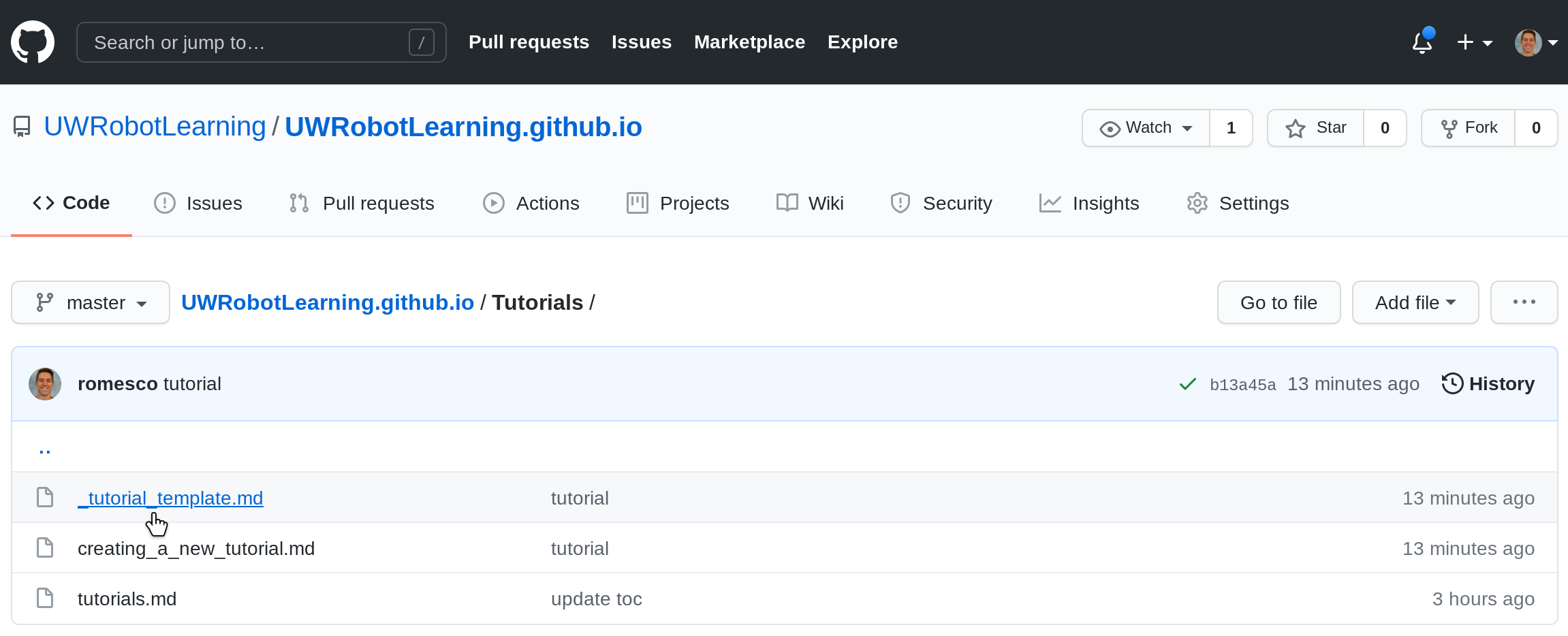
[01] Create New Branch
- Select switch branch by clicking on the current branch,
master. - Type a new branch name. Here we prefix the branch name with
tutorials/. - Click “Create branch`.
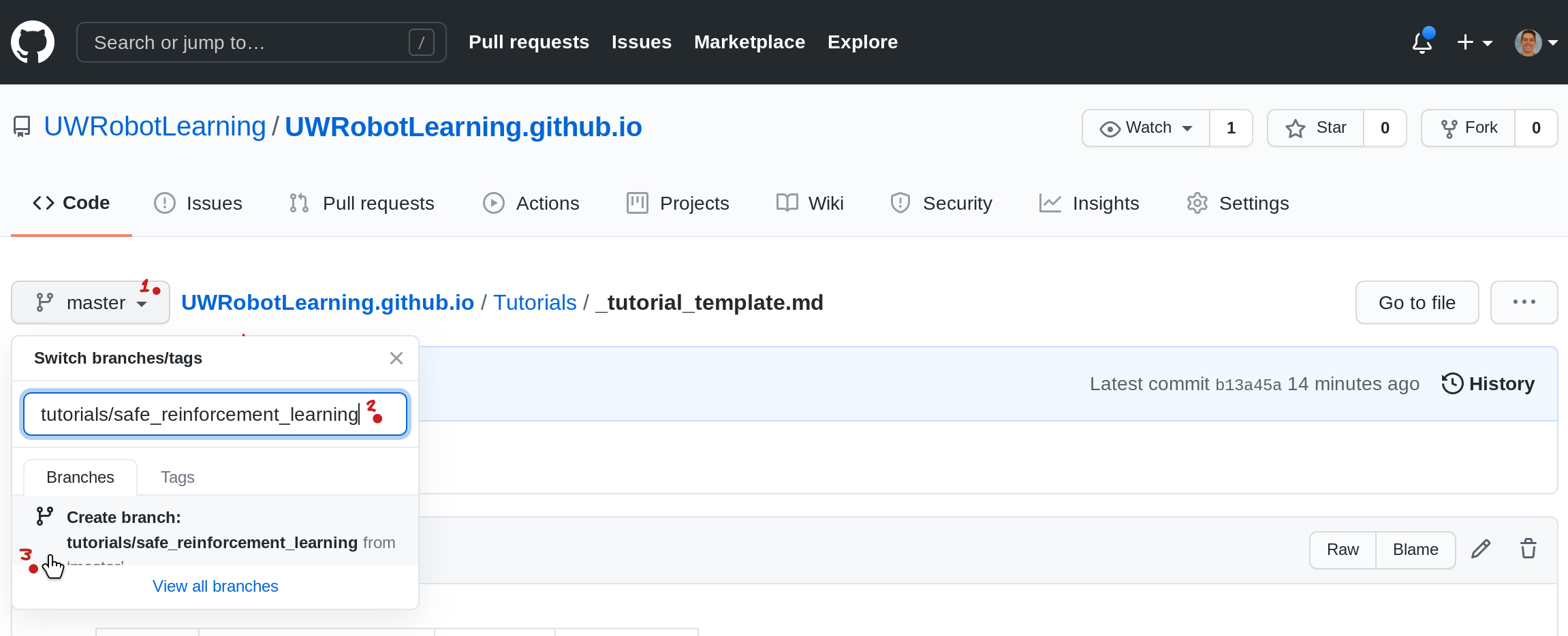
[02] Branch Created
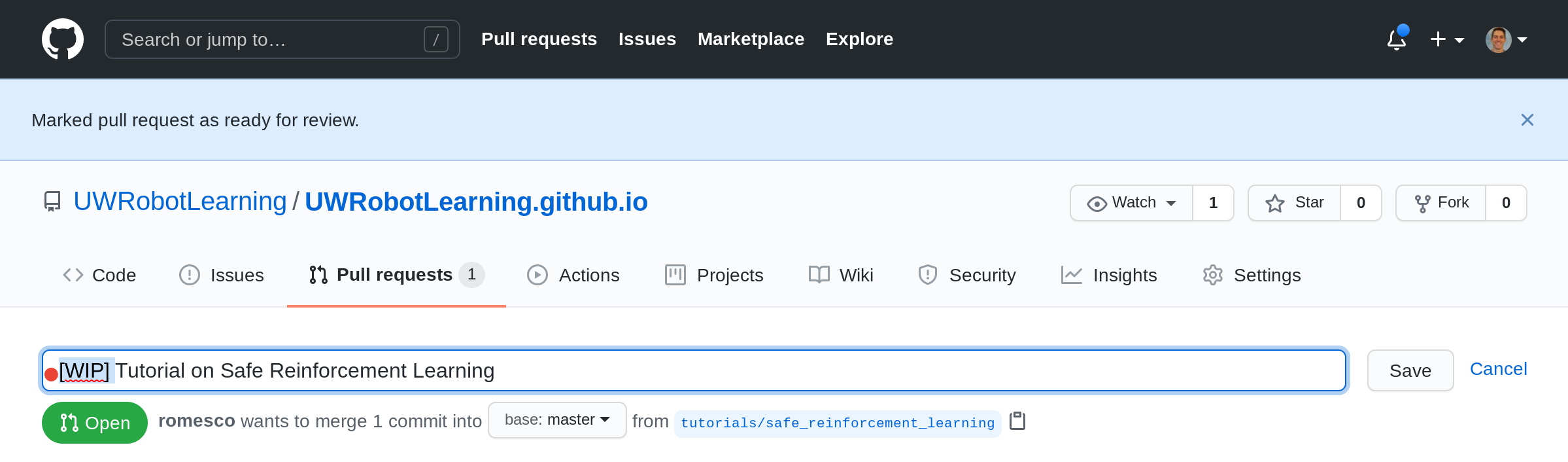
Notice, the branch selection now says tutorials/safe...
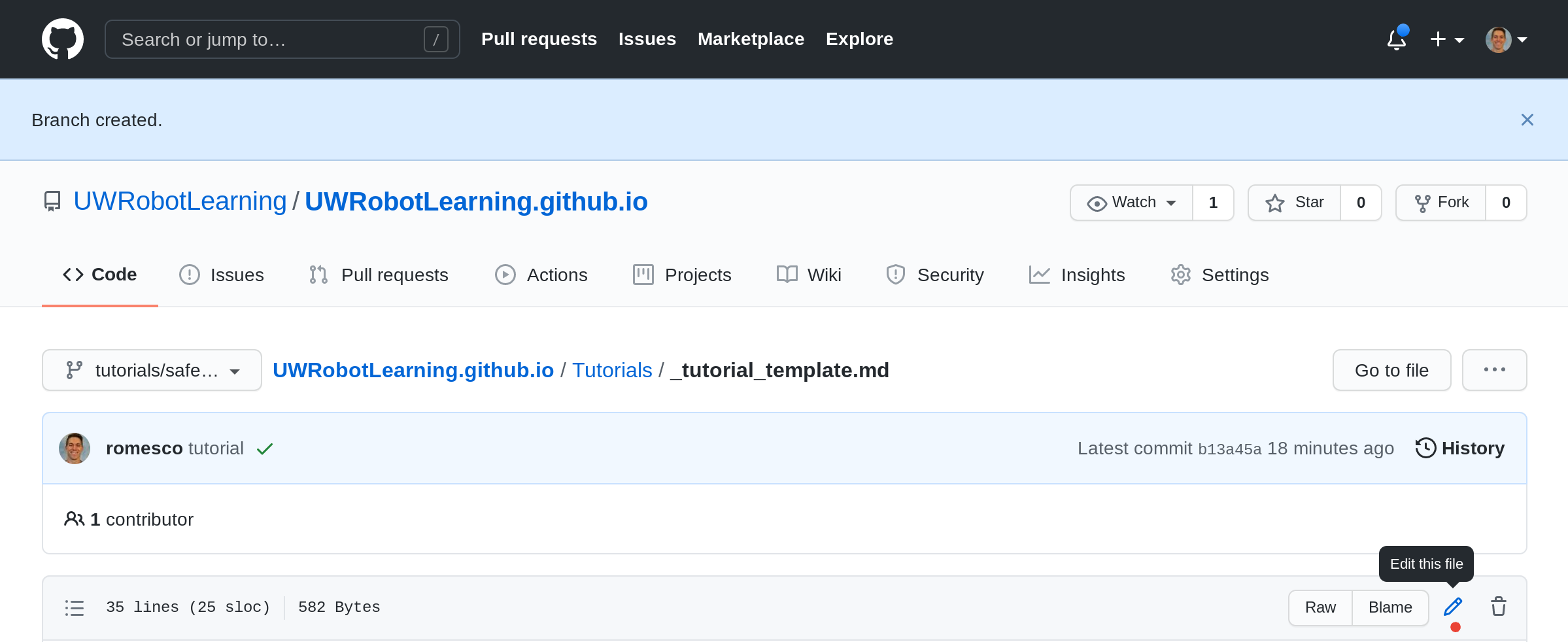
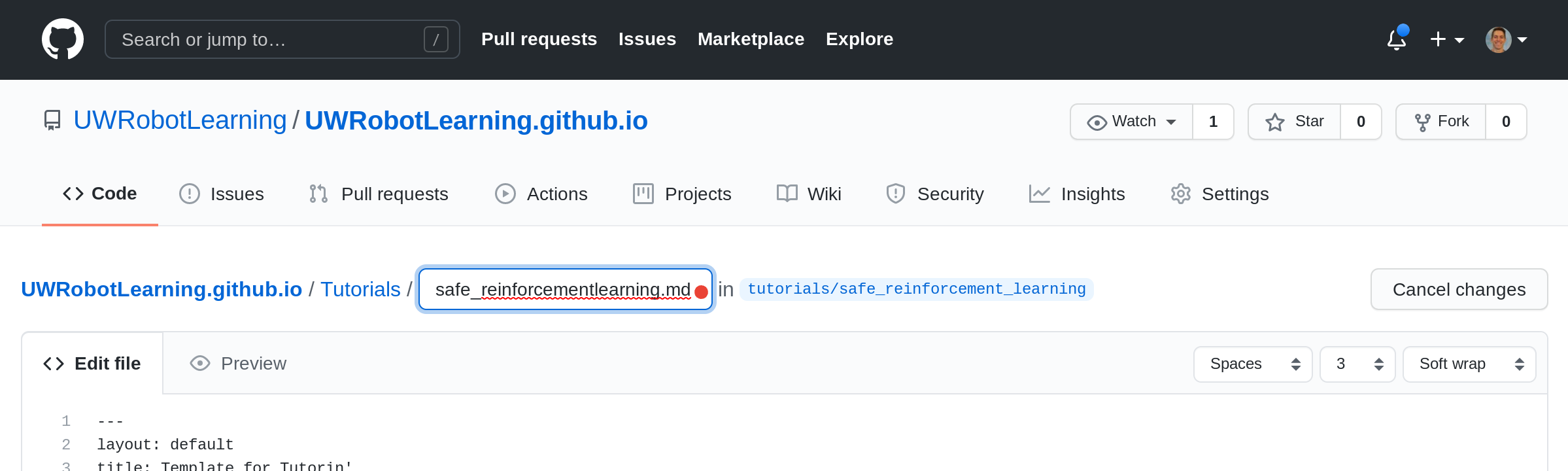
[03] Edit the Filename
Here we change the name from _tutorial_template.md to safe_reinforcementlearning.md.
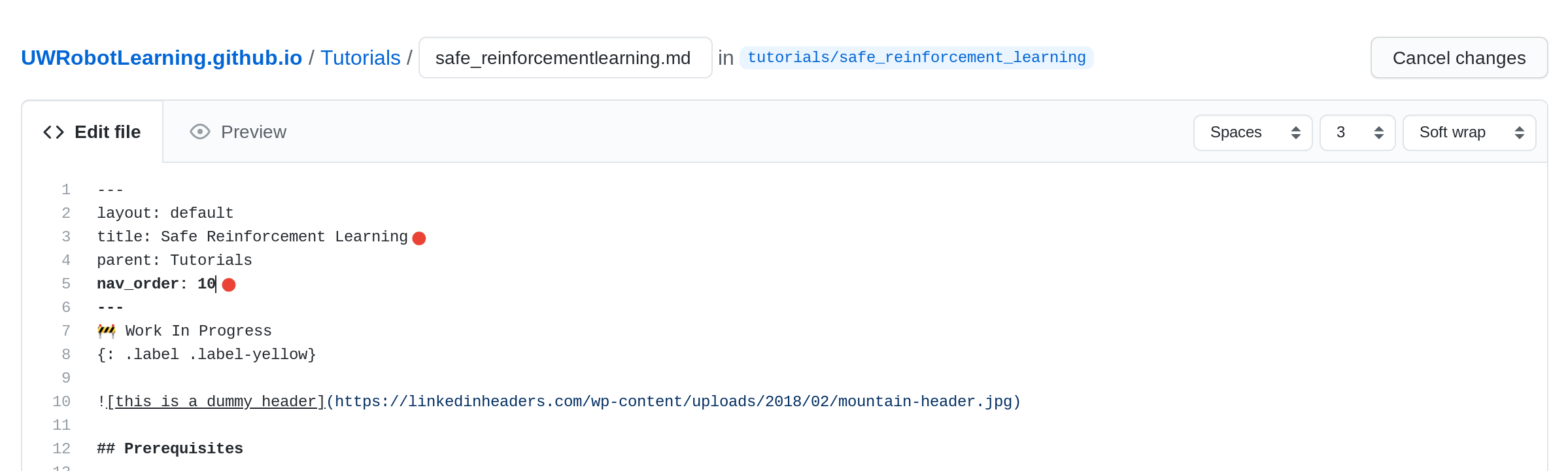
[04] Edit the Frontmatter
Change two fields in the just_the_docs Frontmatter.
- Here we change the
titlefromTemplate for Tutorin'toSafe Reinforcement Learning. - We also change the
nav_orderfrom99to10. This affects the ranking in the nav bar. Lower is higher on the list.
[05] Edit the Content
- Edit the template directly to contain the actual content you’d like to teach to others.
- For tips on markdown, see References.
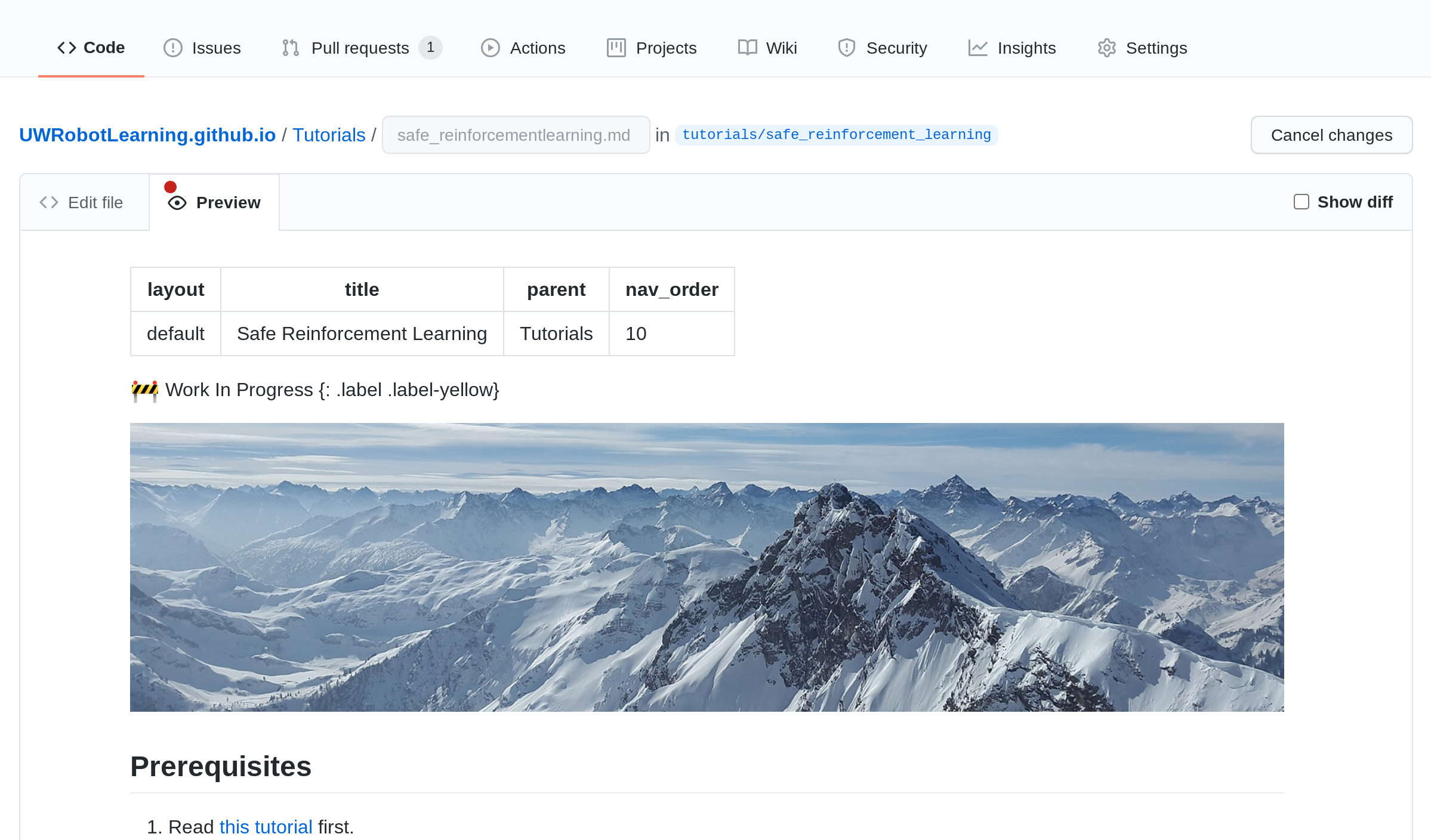
[06] Preview the Content
Click the preview tab to see the content you’ve entered. You can go back and forth between ‘Edit file’ and ‘Preview’ to check your formatting.
[07] [Optional] Remove or Change the Label
If you plan to continue adding to this tutorial at a later date, but would like to share the content added so far, leavel the WIP label and skip this step.
You can also add a different label here like:
🔥 Fire Tutorial
{: .label .label-blue}
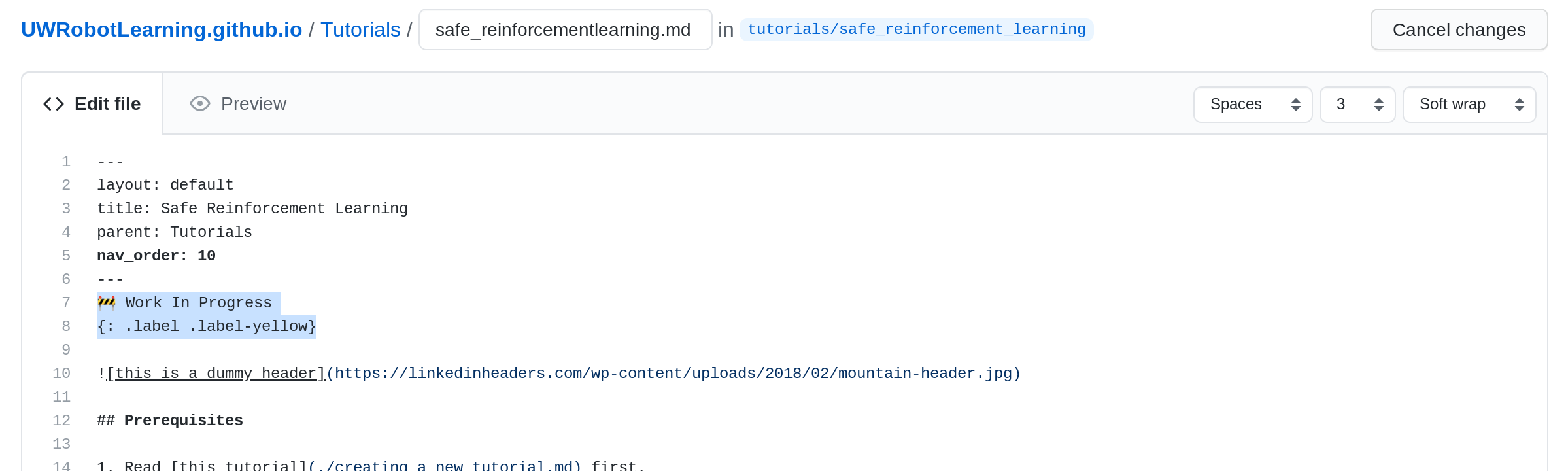
[08] Commit Changes
- Scroll down to the bottom of the page.
- Add a quick comment about your changes.
- Click the green
Commit changesbutton.
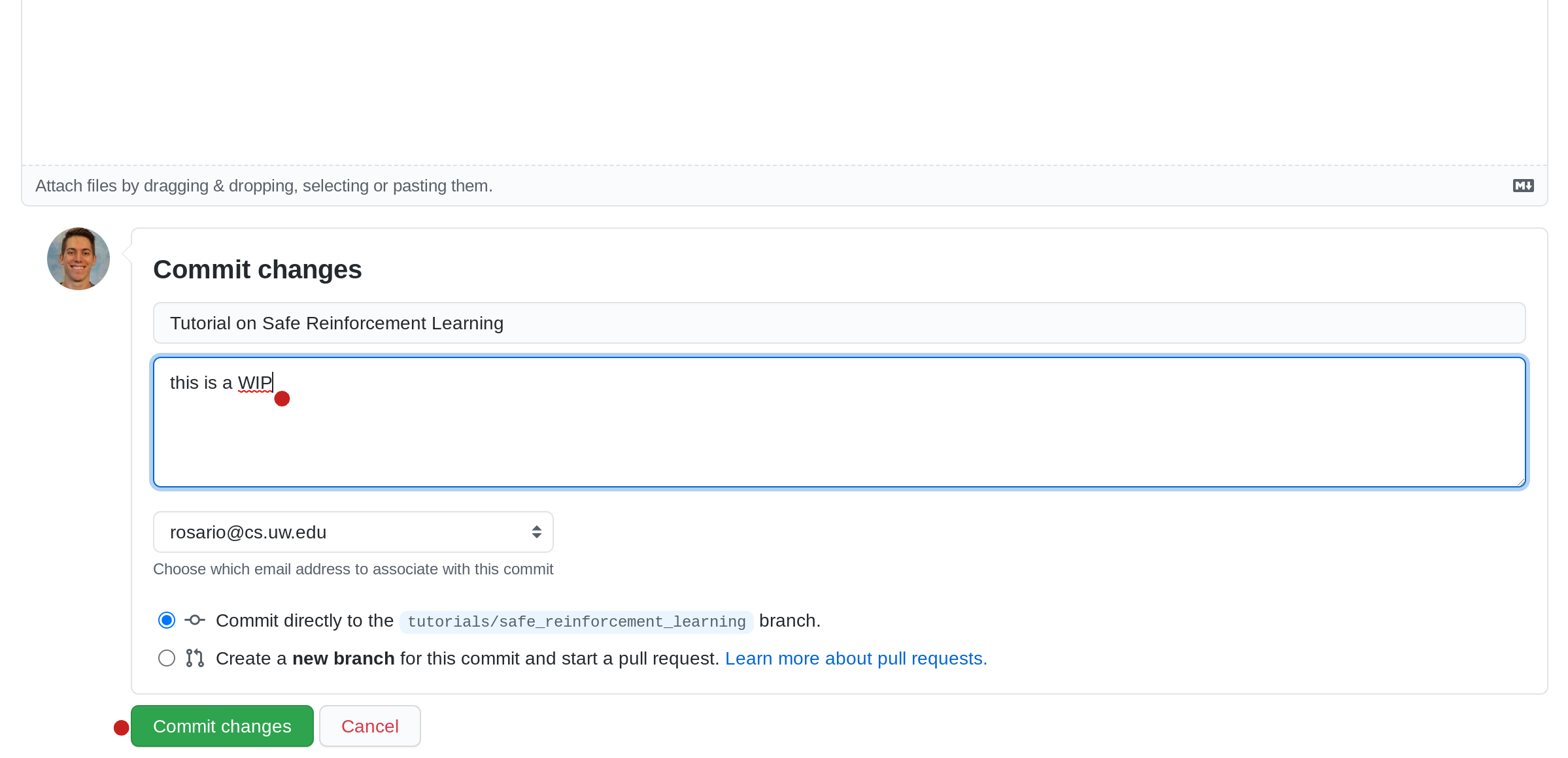
[09] Navigate to Pull Requests
Click the Pull requests Tab.
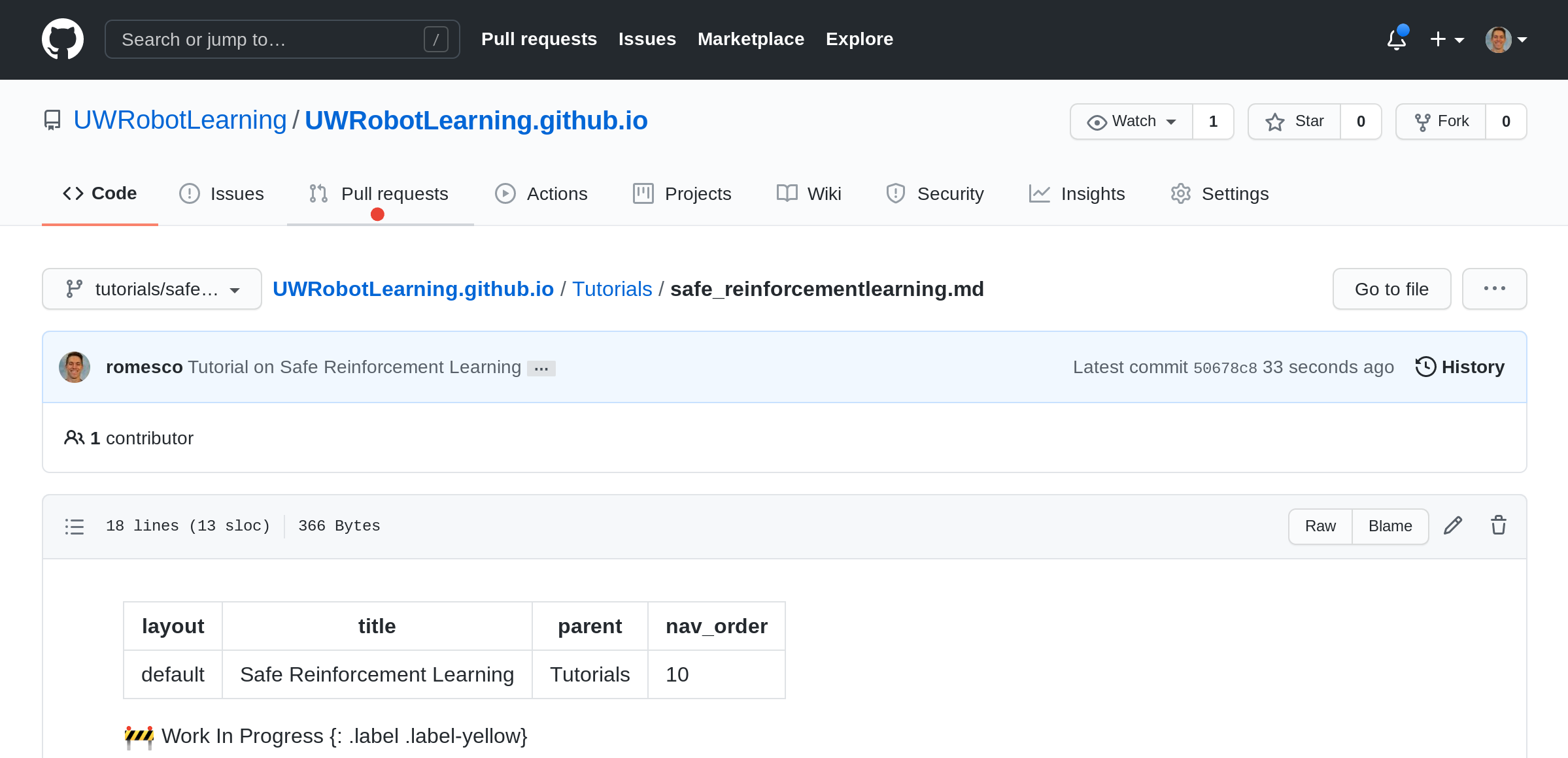
[10] Create Pull Request
You will now create a pull request to merge from the tutorials/safe_reinforcement_learning branch to the master branch.
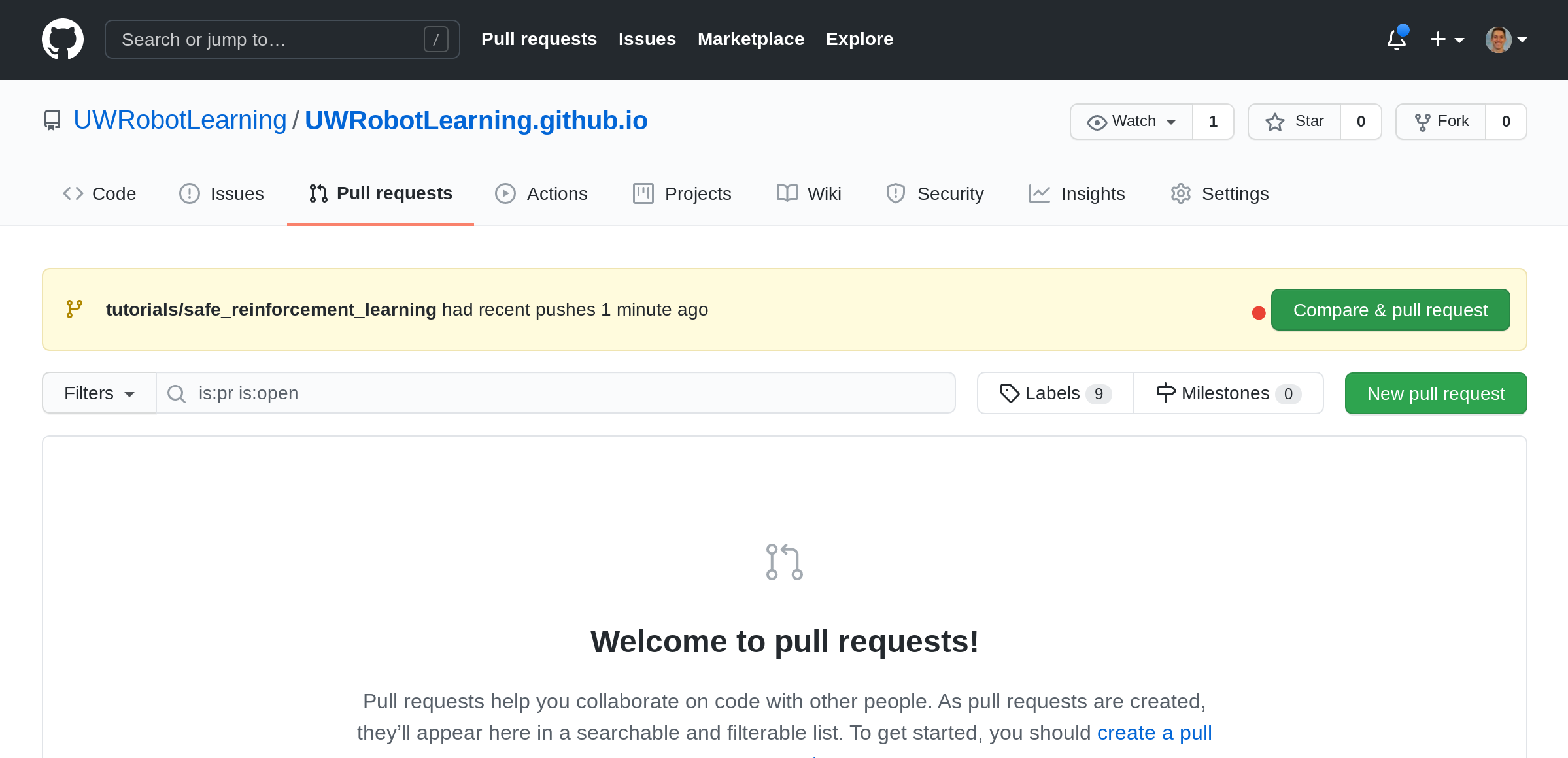
[11] Draft PR or Ready To Go PR
Here, you have two options. File a “Draft PR” or a PR that is ready to merge right away. The purpose of a draft PR is to remain in the PR inbox with the option for other lab members to review without explicitly requesting reviews yet. Typically a Draft PR has the prefix [WIP] which stands for Work in Progress.
Draft:
- Give a title prefixed with
[WIP]. - Click either the drop down to select
Create draft pull request. - Click the green button to submit the draft pull request.
Ready PR:
- Give a title
- Click the
Create pull requestbutton to submit it for review.
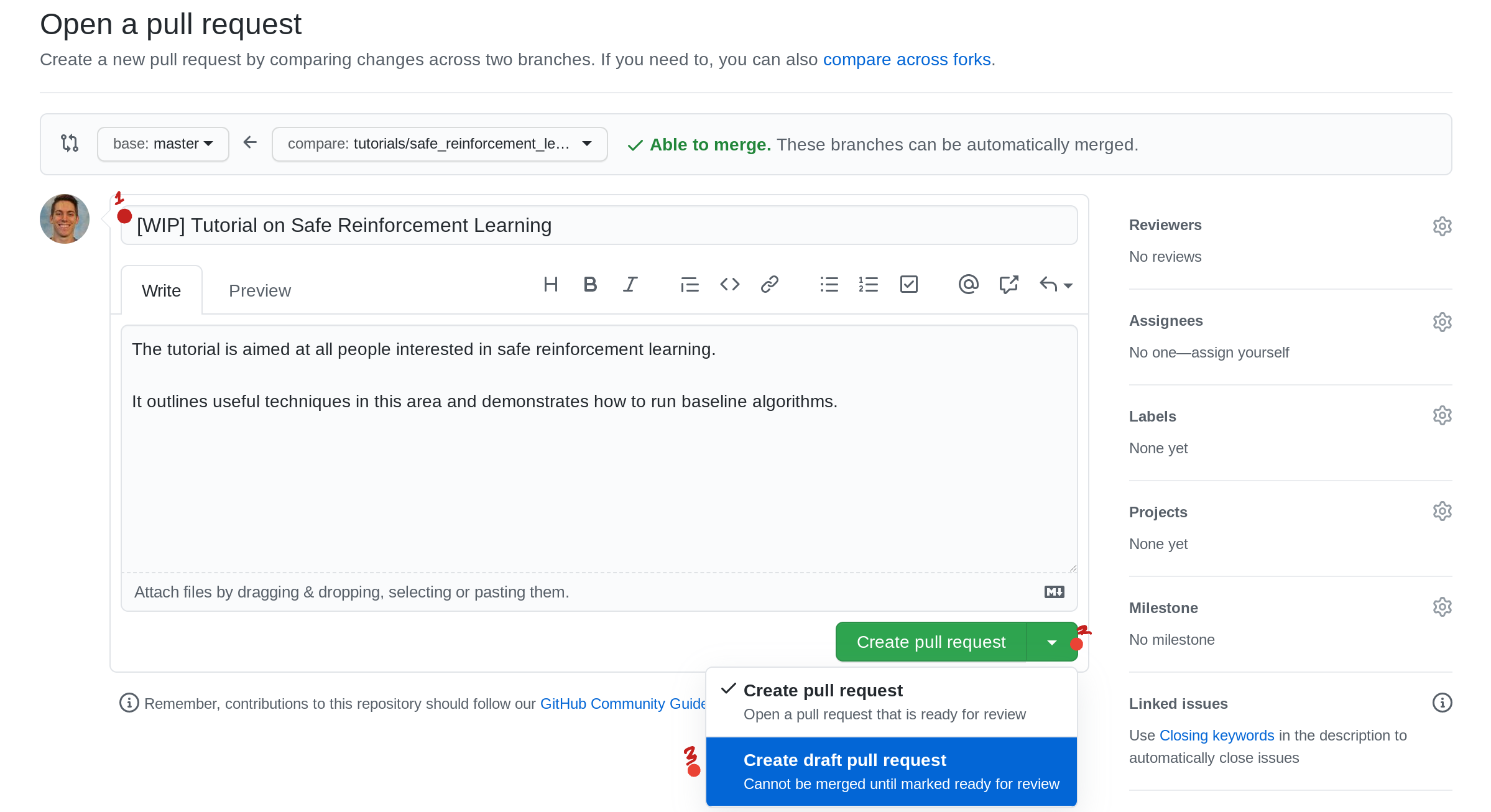
[12] Request a Reviewer
- Click the gear icon.
- Type a lab member’s name to explictly request their review.
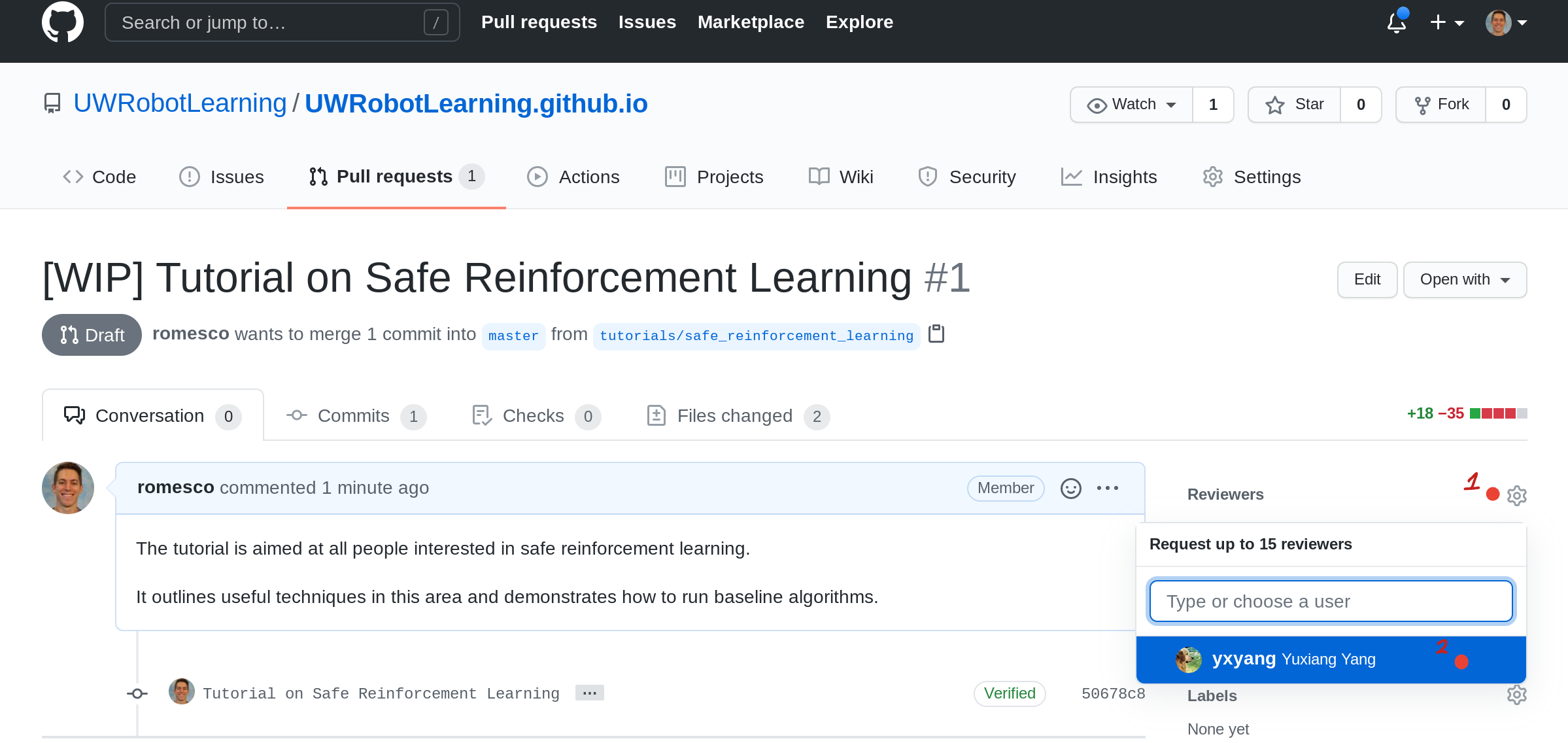
[13] Patiently Await Review
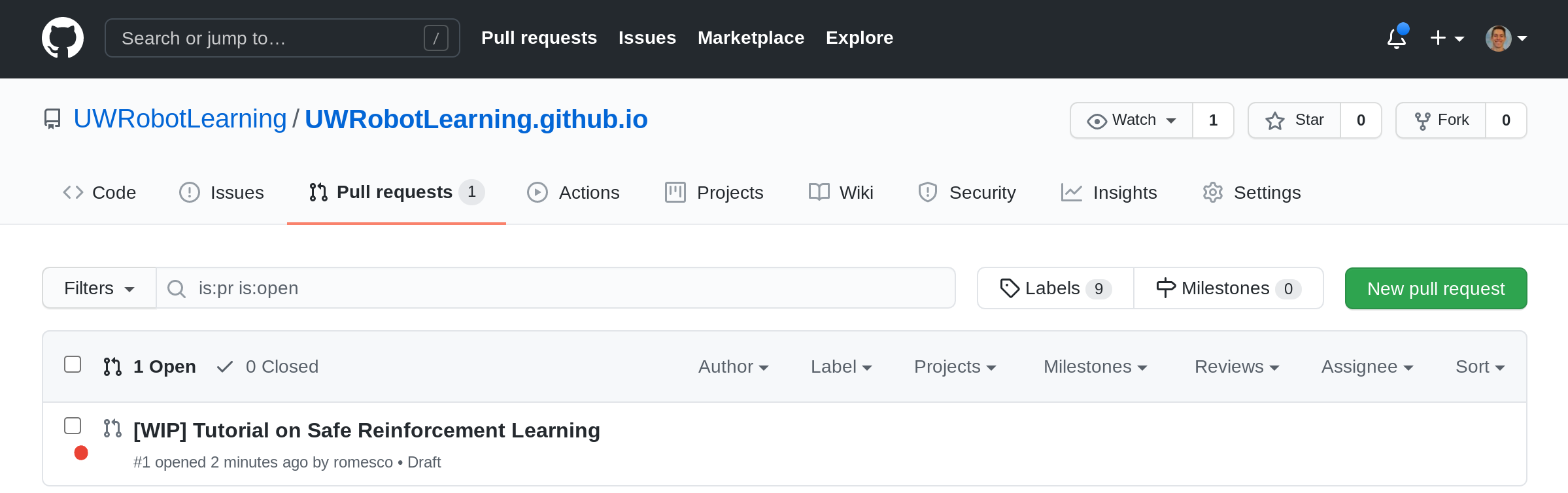
You will now see your PR waiting in the Open List under the Pull requests tab.
[14] Get Your Review and Reply
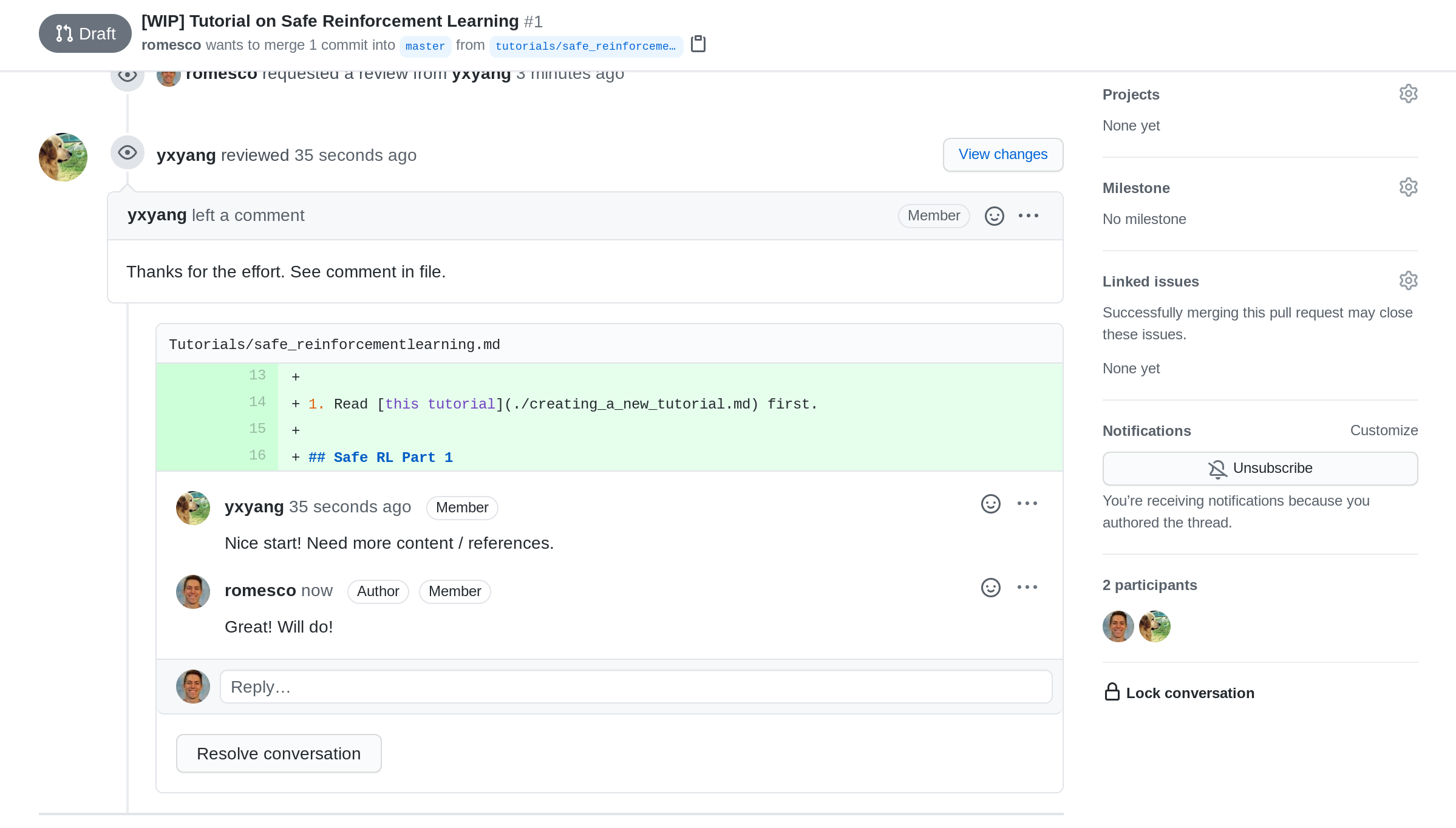
You’ll receive some feedback on your content so far and you will receive one of these:
- Requested changes before approval
- Comments with no explicit approval
- Explicit approval
Feel free to ask questions or ask for clarifications. These PRs are meant to be like fast conversations.
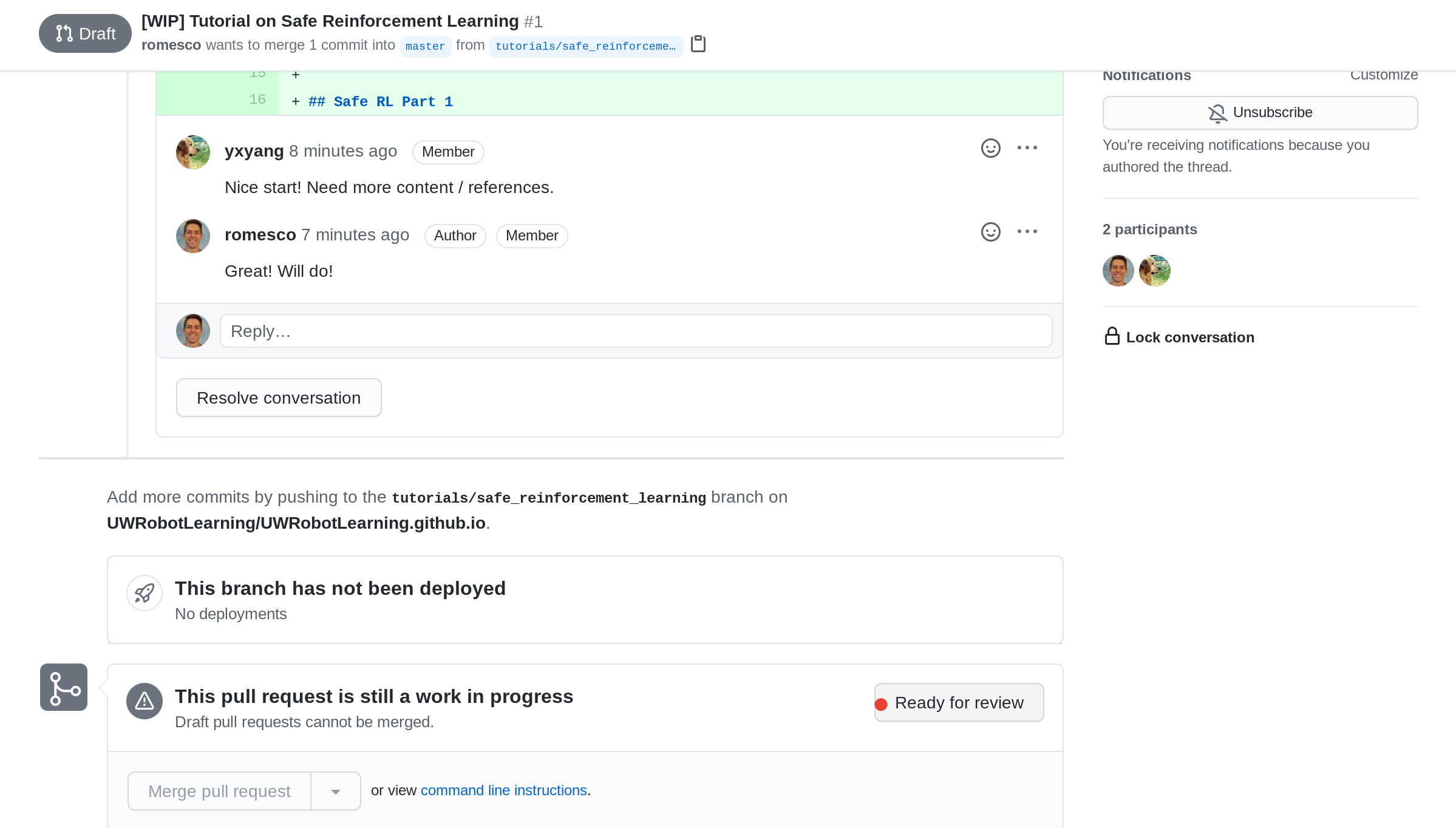
[15] [If Draft] Mark Ready for Full Review
This only applied if the PR was still in draft mode. Click the Read for review button to convert the draft to a full PR.
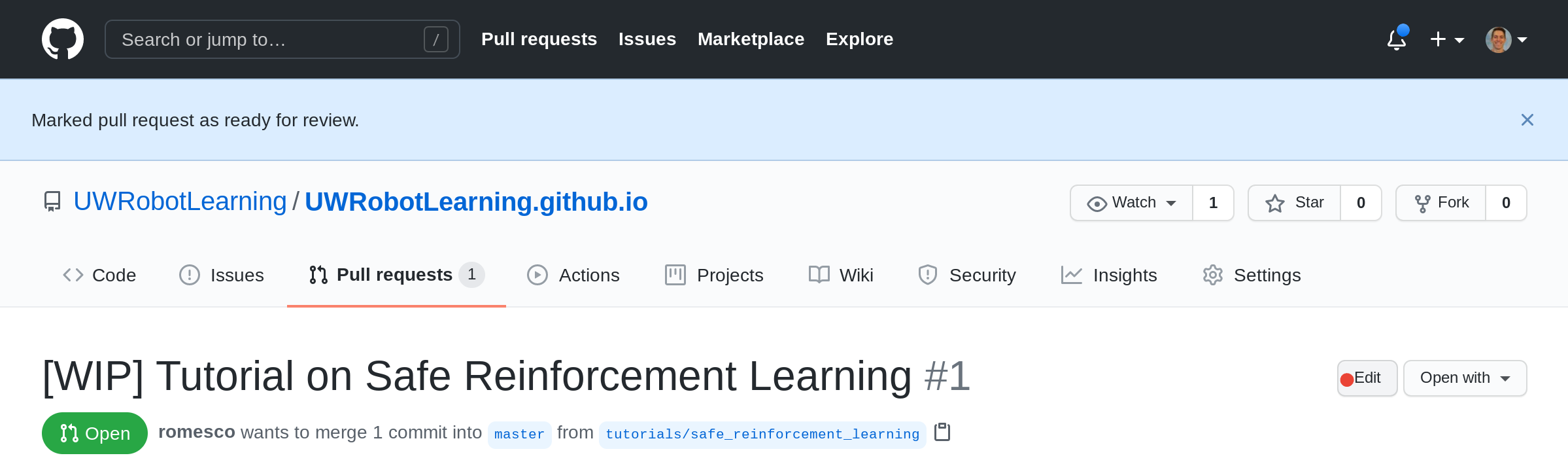
[16] [If Draft] Edit the PR Title
If the PR is changing from Draft to Full, remove the [WIP] prefix from the title by clicking the Edit button.
[17] Await Merge
Finally, ensure this title is something descriptive before it gets merged into master as this will remain in the record of Merged PRs after the merge process is complete. Typically a non-author lab member will approve the final merge.
If the PR-Merge workflow still seems shrouded in mystery, see the Github Workflow Tutorial for more detail.